It is admitted that gaining knowledge of Keynesian Economics and Classical Economics is essential for all economics students. These two theories offer different ways economies work and the government’s position on economic control. As your economics assignment helpers, let us explain these concepts so you can excel.
Foundations of Keynesian Economics: Insights for Economic Assignment Helpers
Keynesian Economics, established by John Maynard Keynes, focuses on the role of government intervention and aggregate demand in the economy.
Government Intervention in Keynesian Economics
According to Keynesian Economics, government interference should be made a large part within and especially during a recession. Keynes pointed out this theoretical insight that an economy can get locked into stagnation, low demand, and high unemployment for a long time without government intervention. Thus, the government can use the availability method by increasing its purchases or reducing taxation rates, which resolves demand deficiency and brings the economy out of recession. Economics assignment helpers explain that this approach is a core component of Keynes’ ideas and is one of the most essential concepts for tutors dealing with economic assignments.
Limits to the Use of Aggregate Demand in Keynesian Economics
The central theme in Keynesian theory is aggregate demand, the total demand for goods and services within the economy. Some economists, called Keynesians, think that cycles depend on changes in total demand. In this regard, Keynesians recommend increasing government expenditures when there is low demand or excess supply so that the available supply can be sold and unemployment reduced, among other things. Students must comprehend this idea once they assess economic policies and their outcomes.
Principles of Classical Economics by Economics Assignment helpers
Important Information that Should be Provided to Help in Doing Economic Assignments
Classical economics, newly emerging from Adam Smith’s work, stresses the idea of markets being automatically self-correcting and the importance of demand-side factors.
Self-Regulating Markets and Its Theory in Classical Economics
Classical economists worked with the economic principle that leave-alone markets can automatically correct. They insisted that markets would self-correct by achieving the employment levels of their citizens and the proper distribution of available resources. In essence, this principle asserts that demand is met by supply (Say’s law), implying that production stimulates economic activity. Generally, economic assignment helpers have to understand the Keynesian views to contrast them with this fundamental principle.
Supply-Side Focus in Classical Economics
Unlike Keynesian Economics, whose central agenda is the demand side of the economy, classical economics is more of the supply side. According to classical economists’ mode of reasoning, in the long run, economic growth is determined by capital deepening, technological progression, and human resource development. Concerning the supply-side factors, a country can attain sustainable development if these factors are enhanced. This focus is essential for students to grasp when discussing policies that improve long-term economic growth prospects.
Key Differences Between Keynesian and Classical Economics: Economics assignment helpers
In this context, the students form two groups, a breakdown to help those assigned to the economic assignment.
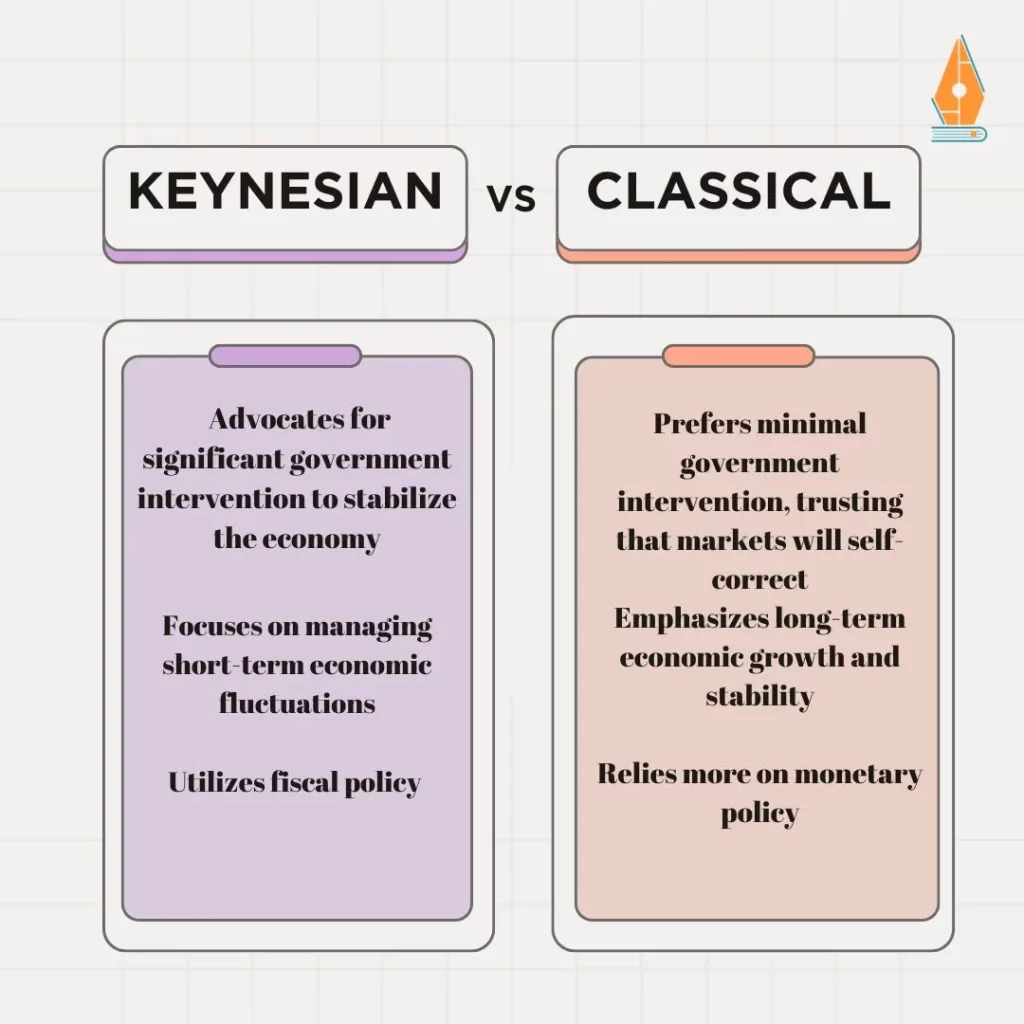
This is because economics students and those who assist in completing economic assignments must distinguish between these two theories.
The function of the government in Keynesian is compared to that of the classical economic system.
Keynesian Economics: Those who believe in volatility and featuring strong government action to regulate business cycles and stabilize an economy in a recession.
Classical Economics: It is applied when the government interferes little with the market, believing that markets are self-correcting.
Economics assignment helpers should explain that these varying stances on government dealings color the positions advanced concerning policies and financial results.
Economic Drivers in Keynesian and Classical Economics
Keynesian Economics: Outcome stresses the role of the increase in aggregate demand for stimulating economic activity and creating employment opportunities.
Classical Economics: Stresses the effects, especially the supply-side effects of production and technological changes, as the most significant growth propellers.
Students need to be informed of these varying objectives when trying to understand economic theories or their ability to be applied.
Comparing of Policy Tools in Keynesian VS Classical Economy
Keynesian Economics: Controls the government’s spending and taxation to affect demand for goods.
Classical Economics: It depends more on stand-alone or monetary policy and other self-correcting mechanisms inherent in open economies.
Economic assignment helpers need to ensure that students are able to explain how these policy tools are used distinctively in each theory of analysis.
Flexibility of Price and Wage in Keynesian as Compared To Classical Economics
Keynesian Economics: states that prices and wages in the economy are often rigid and slow to change, meaning individuals spend much time without jobs.
Classical Economics: The belief that the prices of goods and services and wages can adjust quickly to cover the shocks and levels of disequilibrium can be corrected soon in the markets.
Pointing out these differences in price and wage flexibility will help students comprehend the consequences of unemployment and inflation.
Applying Keynesian and Classical Economics: Harvard Style Sources for Economic Assignment Helper of Real-World Examples
For general analysis, such students should also consider how these theories work when solving economics-related problems.
Key Keynesian and Classical Economics: Policy Implications
These policies are usually used particularly in periods of economic turmoil, as observed in the financial year 2008 when most governments worldwide used +ve fiscal multipliers. On the other hand, classical economics might be used in periods of economic stability, entailing the reduction of state interference and the promotion of free-market policies. The economic assignment helpers and tutors can use these examples to explain the relationship between different economic theories and policy outcomes.
Some of the real-life applications for conducting economic assignments include;
While approaching the tasks, consider how these theories give insight into present economic processes. For example, compare and evaluate Keynesian or classical principles evident in the various governments’ handling of economic recessions. Knowledge of these applications helps with the assignments and is essential in realizing the consequences of monetary policies. These features make the book valuable for students applying the theory in practice.
Conclusion: Accomplishing Keynes and Classicals in Economics with an Economic Assignment Helper
Therefore, as we draw this conclusion, we will note that Keynesian and Classical Economics present quite a different picture of how economies work and the government’s place within them. While Keynesian Economics focuses on short-term fluctuations and the importance of demand, Classical Economics emphasizes long-term growth driven by supply-side factors. As an economics assignment helpers, understanding these differences is critical to excelling in your studies and applying these concepts to real-world scenarios.
Don’t hesitate to contact our economics assignment helpers for personalized assistance with your economics assignments. We’re here to help you succeed!


